TriQDef: Disrupting Semantic and Gradient Alignment to Prevent Adversarial Patch Transferability in Quantized Neural Networks
Published in ICLR, 2026
Links
- Paper: OpenReview
Overview
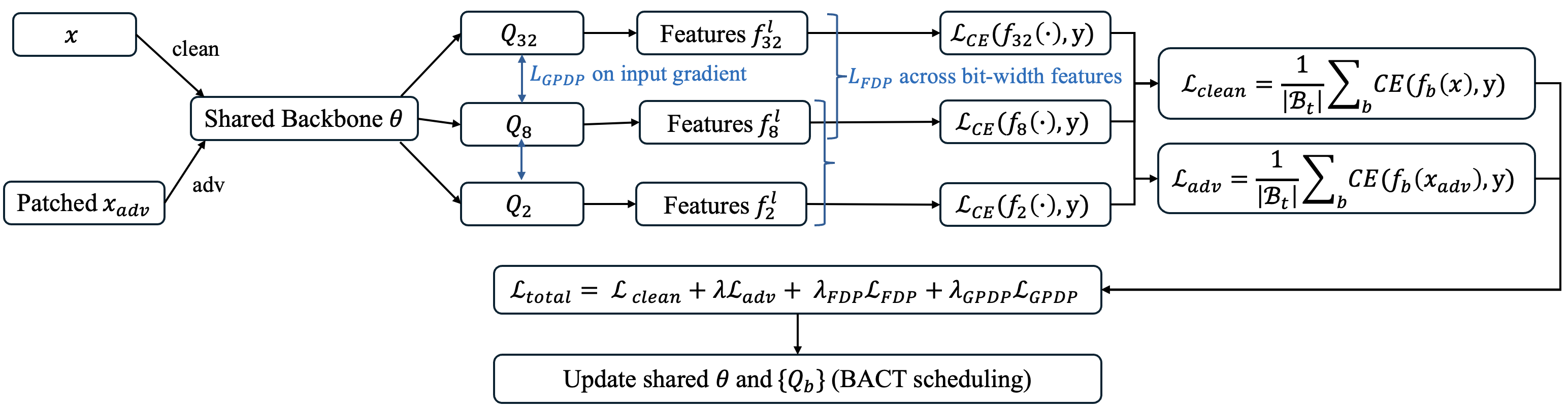
Abstract
Quantized Neural Networks (QNNs) are widely deployed in edge and resourceconstrained environments for their efficiency in computation and memory. While quantization distorts gradient landscapes and weakens pixel-level attacks, it offers limited robustness against patch-based adversarial attacks—localized, highsaliency perturbations that remain highly transferable across bit-widths. Existing defenses either overfit to specific quantization settings or fail to address this crossbit vulnerability. We propose TriQDef, a tri-level quantization-aware defense framework that disrupts the transferability of patch-based attacks across QNNs. TriQDef integrates: (1) a Feature Disalignment Penalty (FDP) that enforces semantic inconsistency by penalizing perceptual similarity in intermediate features; (2) a Gradient Perceptual Dissonance Penalty (GPDP) that misaligns input gradients across quantization levels using structural metrics such as Edge IoU and HOG Cosine; and (3) a Joint Quantization-Aware Training Protocol that applies these penalties within a shared backbone jointly optimized across multiple quantizers. Extensive experiments on CIFAR-10 and ImageNet show that TriQDef lowers Attack Success Rates (ASR) by over 40% on unseen patch and quantization combinations while preserving high clean accuracy. These results highlight the importance of disrupting both semantic and perceptual gradient alignment to mitigate patch transferability in QNNs.
Key Contributions
- We conduct, to our knowledge, the first systematic study of patch-based transferability in QNNs, demonstrating that adversarial patches remain highly effective across quantization levels, including 2-bit regimes.
- We propose TriQDef, a tri-component defense targeting both feature and gradient alignment, explicitly designed to prevent cross-bit patch generalization.
- We introduce perceptual alignment metrics (Edge IoU and HOG Cosine Similarity) as theoretically justified tools to quantify and disrupt semantic and gradient-level alignment across bit-widths. These metrics provide a principled alternative to cosine similarity by capturing structural and textural alignment that underlies patch transferability in QNNs.
- Our approach reduces attack success rate (ASR) by over 40% on unseen patch and quantization configurations across CIFAR-10 and ImageNet, outperforming PBAT and DWQ with around 2% drop in clean accuracy.
- Ablation studies validate the complementary role of each module and reveal that quantization alone does not sufficiently alter the shared attack surface, highlighting the need for targeted perceptual and structural misalignment.
Citation
```bibtex @inproceedings{guesmi2026triqdef, title={TriQDef: Disrupting Semantic and Gradient Alignment to Prevent Adversarial Patch Transferability in Quantized Neural Networks}, author={Guesmi, Amira and Ouni, Bassem and Shafique, Muhammad}, booktitle={International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR)}, year={2026} }

