SSAP: A Shape-Sensitive Adversarial Patch for Monocular Depth Estimation
Published in IROS, 2024
Links
- Paper: IROS
Overview
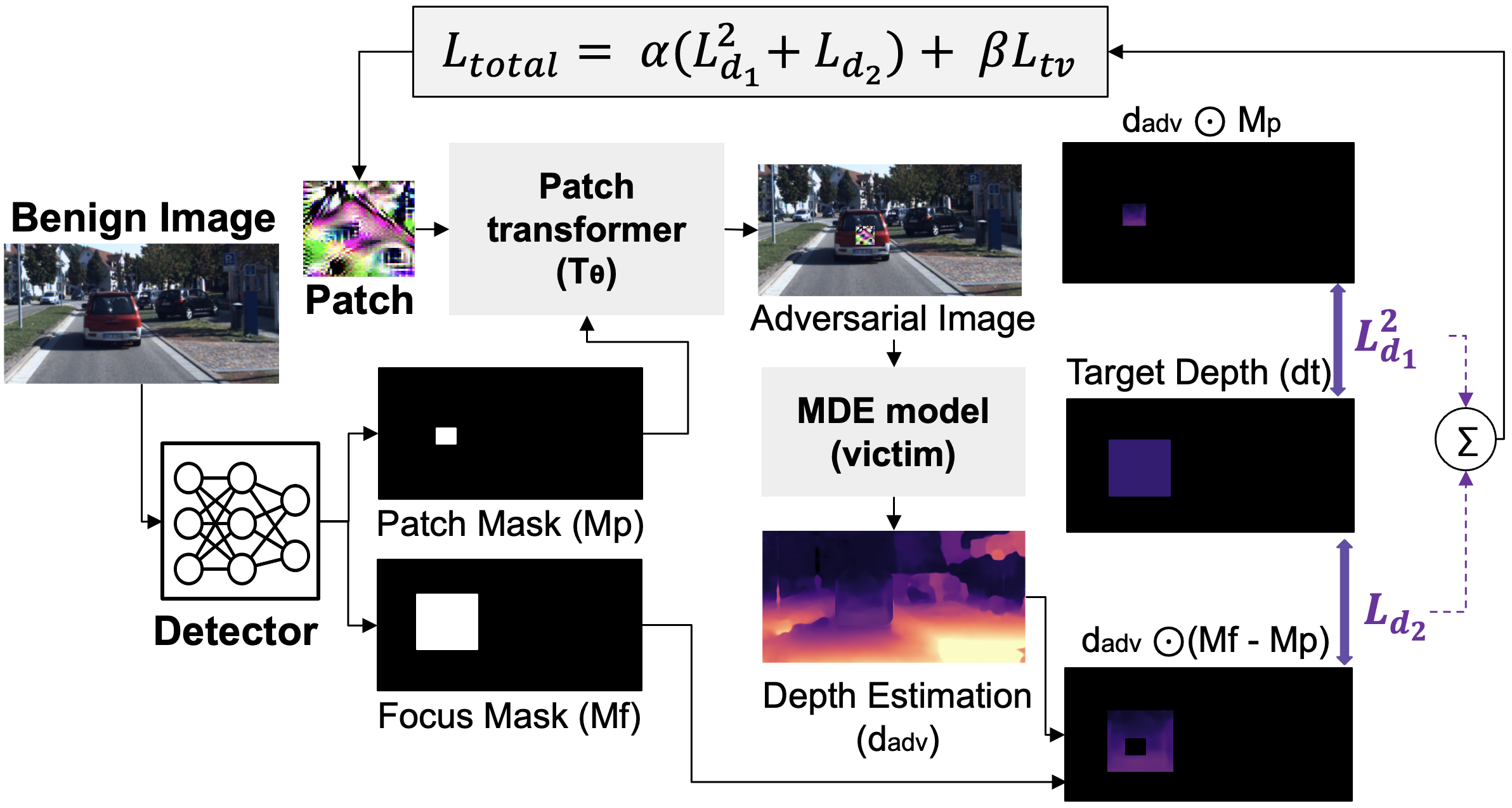
Abstract
Monocular Depth Estimation (MDE) plays a critical role in autonomous driving, robotics, and intelligent navigation systems, where accurate perception of scene geometry is essential for safe decision-making. Despite significant advances in deep learning–based depth estimation models, their robustness against adversarial attacks remains largely unexplored.
In this paper, we introduce SSAP — a Shape-Sensitive Adversarial Patch designed to comprehensively disrupt monocular depth estimation systems. Unlike conventional adversarial patches that primarily affect overlapping pixels, SSAP leverages object shape priors to propagate depth distortion across the full spatial extent of the target object.
By optimizing a penalized depth loss under realistic physical transformations — including scale variation, rotation, viewpoint shifts, and illumination changes — SSAP induces severe depth misestimation and even object disappearance in predicted depth maps. Extensive experiments across CNN-based and Transformer-based MDE architectures demonstrate that SSAP can produce depth estimation errors exceeding 0.5 while affecting up to 99% of the object region.
These findings highlight critical vulnerabilities in perception systems deployed in autonomous environments and underscore the urgent need for robust defenses against shape-aware physical adversarial attacks.
Key Contributions
We propose SSAP, the first shape-sensitive adversarial patch designed specifically to attack monocular depth estimation systems rather than object classification or detection pipelines.
We introduce a shape-aware optimization objective that propagates perturbation influence beyond direct pixel overlap, enabling large-scale depth distortion across entire object structures.
We develop a penalized depth loss formulation that explicitly maximizes depth estimation error while preserving physical realizability under environmental transformations.
We demonstrate strong attack effectiveness across diverse MDE architectures, including both convolutional and Transformer-based depth estimation networks.
We conduct comprehensive evaluations under physical-world transformations such as scale variation, viewpoint shifts, and illumination changes, validating SSAP’s robustness in real deployment conditions.
We show that SSAP can induce object disappearance and severe distance misestimation, posing critical safety risks in autonomous navigation scenarios.
Citation
```bibtex @inproceedings{guesmi2024ssap, title = {SSAP: A Shape-Sensitive Adversarial Patch for Comprehensive Disruption of Monocular Depth Estimation}, author = {Guesmi, Amira and Hanif, Muhammad Abdullah and Alouani, Ihsen and Ouni, Bassem and Shafique, Muhammad}, booktitle = {IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS)}, year = {2024} }

