DRIFT: Divergent Response in Filtered Transformations for Robust Adversarial Defense
Published in ICLR, 2026
Links
- Paper: OpenReview
Overview
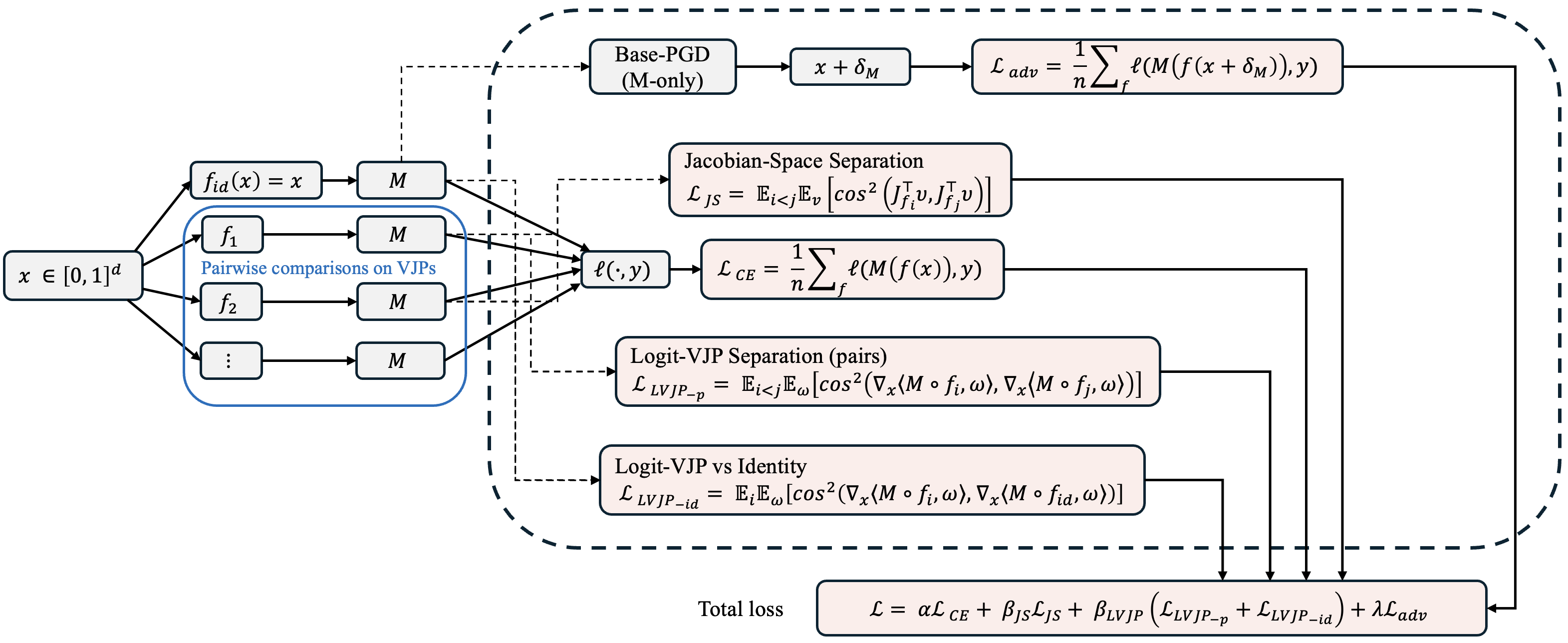
Abstract
Deep neural networks remain highly vulnerable to adversarial examples, and most defenses collapse once gradients can be reliably estimated. We identify gradient consensus—the tendency of randomized transformations to yield aligned gradients—as a key driver of adversarial transferability. Attackers exploit this consensus to construct perturbations that remain effective across transformations. We introduce DRIFT (Divergent Response in Filtered Transformations), a stochastic ensemble of lightweight, learnable filters trained to actively disrupt gradient consensus. Unlike prior randomized defenses that rely on gradient masking, DRIFT enforces gradient dissonance by maximizing divergence in Jacobian- and logitspace responses while preserving natural predictions. Our contributions are threefold: (i) we formalize gradient consensus and provide a theoretical analysis linking consensus to transferability; (ii) we propose a consensus-divergence training strategy combining prediction consistency, Jacobian separation, logit-space separation, and adversarial robustness; and (iii) we show that DRIFT achieves substantial robustness gains on ImageNet across CNNs and Vision Transformers, outperforming state-of-the-art preprocessing, adversarial training, and diffusionbased defenses under adaptive white-box, transfer-based, and gradient-free attacks. DRIFT delivers these improvements with negligible runtime and memory cost, establishing gradient divergence as a practical and generalizable principle for adversarial defense.
Key Contributions
- We formalize the concept of gradient consensus and prove that reducing gradient alignment across transformations directly lowers adversarial transferability.
- We propose DRIFT, the first differentiable and adversarially trained filter-ensemble defense that explicitly enforces gradient divergence without modifying or retraining the backbone classifier.
- We demonstrate on ImageNet-scale models (ResNet-v2, Inception-v3, DeiT-S, ViT-B/16) that DRIFT consistently outperforms state-of-the-art transformation-based and stochastic defenses against strong adaptive attacks, including PGD-EoT, AutoAttack, transfer-based attacks, and BPDA.
Citation
```bibtex @inproceedings{guesmi2026drift, title={DRIFT: Divergent Response in Filtered Transformations for Robust Adversarial Defense}, author={Guesmi, Amira and Shafique, Muhammad}, booktitle={International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR)}, year={2026} }

