Defensive Approximation: Securing CNNs using Approximate Computing
Published in ASPLOS, 2021
Links
- Paper: OpenReview
Overview
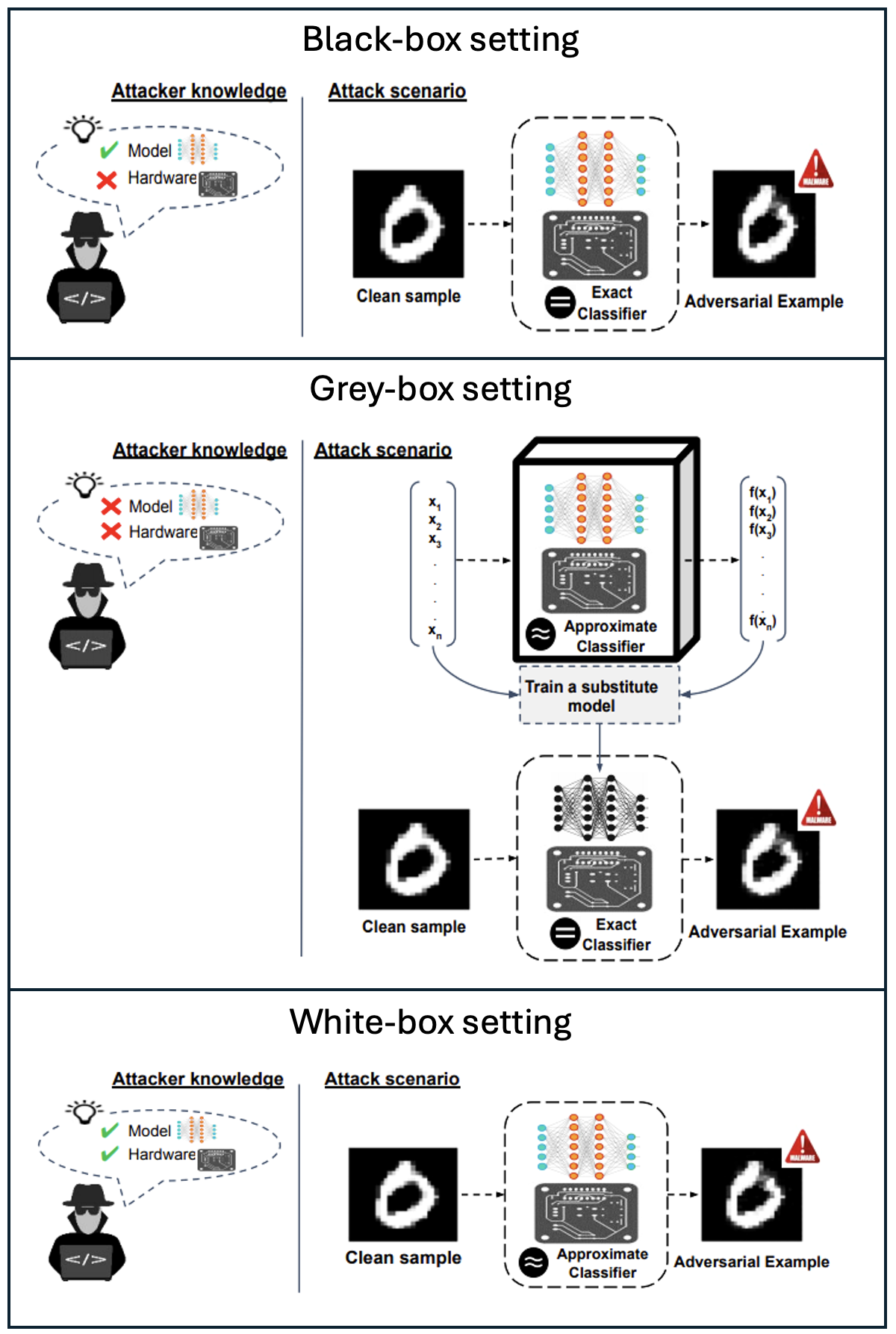
Defensive Approximation (DA) is the first work to demonstrate that hardware-supported approximate computing can be used as an effective defense against adversarial attacks on deep neural networks.
Instead of modifying training or preprocessing inputs, DA injects data-dependent approximation noise directly inside CNN computations, fundamentally disrupting adversarial transferability while preserving accuracy and improving efficiency.
Abstract
Adversarial attacks pose a serious threat to machine learning systems deployed in safety- and security-critical domains.
This paper proposes Defensive Approximation, a novel defense mechanism that leverages approximate computing at the hardware level to improve robustness of convolutional neural networks (CNNs) against adversarial attacks.
By replacing exact floating-point multipliers with aggressively approximate ones, the proposed approach introduces input-dependent perturbations throughout the model, significantly reducing attack transferability in gray-box, black-box, and even white-box settings.
Importantly, this robustness is achieved without retraining, while simultaneously reducing energy consumption and latency.
Extensive experiments on MNIST and CIFAR-10 demonstrate robustness improvements of up to 99% against strong transferability-based attacks, with up to 50% energy savings.
Key Contributions
- First hardware-level adversarial defense using approximate computing
- Strong robustness against:
- Transferability attacks
- Black-box attacks
- White-box attacks
- No retraining or model modification required
- Significant energy and latency reduction
- Improves model confidence while preserving accuracy
Experimental Highlights
- Robustness gains up to 99% against strong transfer attacks
- White-box attacks require substantially higher perturbation budgets
- Maintains baseline accuracy on clean inputs
- Up to 50% energy savings due to simplified arithmetic
Publication
- Amira Guesmi, Ihsen Alouani, Khaled N. Khasawneh, Mouna Baklouti,
Tarek Frikha, Mohamed Abid, Nael Abu-Ghazaleh - Defensive Approximation: Securing CNNs using Approximate Computing
- ASPLOS 2021
- 📄 Paper (ACM DL)
Related Research Directions
This work laid the foundation for later research on:
- Robustness of quantized and approximate neural networks
- Hardware–software co-design for AI security
- Transferability disruption via non-deterministic computation
